Feedback Control on KUKA youBot
MATLAB, Robot Dynamics, Feedback Control, Feedforward Control, Mobile Manipulator, CoppeliaSim
Authors: Allen Liu
Project Description
This project is to implement the feedforward/feedback control over the KUKA youBot to pick up a cube and place it at another place in the world.
Goal
The goal of this project is to simulate the dynamics of the KUKA youBot in CopeliaSim and design the optimal controller given 3 scenarios: Best, Overshoot and New Task, in finding the values of proportinal gain Kp and integral gain Ki for each task.
Best: The robot follows the planned path without any overshoot and steady-state error.Overshoot: The robot reaches the goal with zero steady-state error but overshoots along the way.New Task: The robot follows the planned path to a new goal without overshoot and steady-state error.
Structure
This overall project can be divided into 3 tasks: Kinematics, Path Planning and Feedback Control:
Kinematics: The motion of the robot, used for simulation, how the robot platform will perform with given wheel speed.Path Planning: Planned the path for the end-effector to perform the given task of pick-and-place.Feedback Control: AppliedPIcontrol withFeedforward Controlto control the robot joints so that the end-effector follows the planned trajectory.
Kinematic of the Mobile Platform
The KUKA youBot is a 4-wheel mobile robot, where each wheel can either moving in a stright-line or sliding sideways. The goal is to find the platform speed in x, y direction and the angular speed based on the speed of four wheels. The kinematics of the mobile platform can be modeled as:
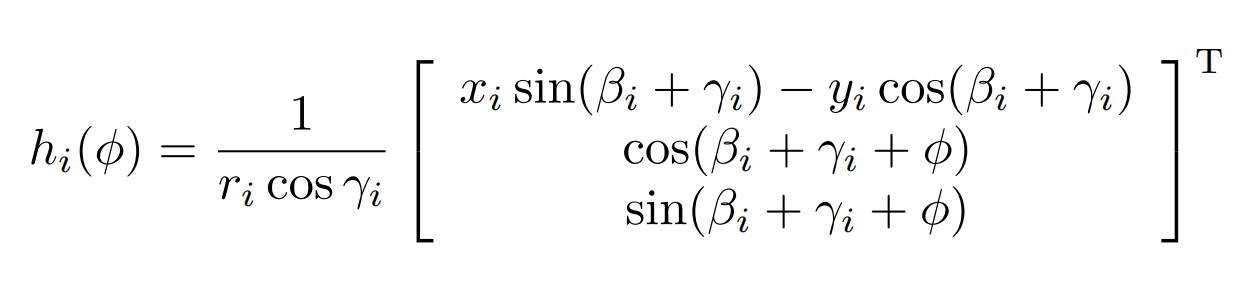
And then by apply this model into the relationship between the q_dot, which is [x_dot, y_dot, theta_dot] and wheel speed vector u, we can get the platform speed based on the wheel speed:
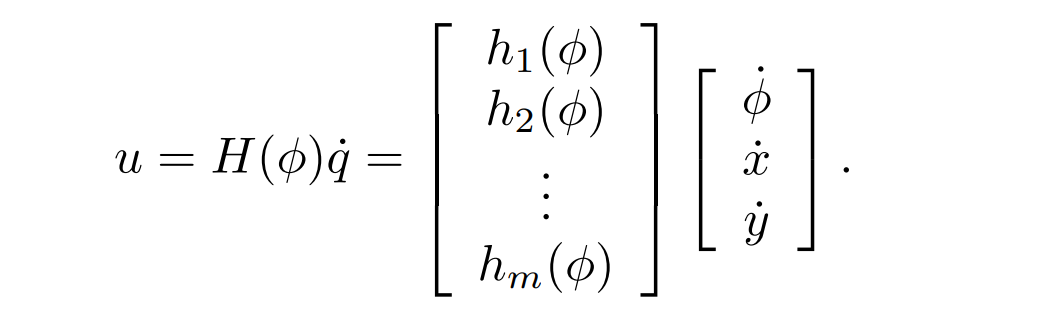
Cartesian Path Generator
To find the path from the start to the goal, I used the cartesian path planning to generate a 5th order cartesian path so that the robot starts and ends with zero accelerations. The path consists of 6 parts:
- From home pose to the standoff pose relative to the start pose of the cube.
- From standoff to reach to cube to grab it.
- After grabing it, move back up to the stand-off pose.
- Go to the stand-off pose relative to the goal pose of the cube.
- Go to the cube final pose and release it.
- Go back to the stand-off pose relative to the goal pose of the cube.
Feedback Control of the KUKA youBot
The controller of the robot is shown as the equation below and the flowchart below:
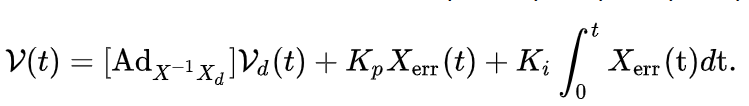
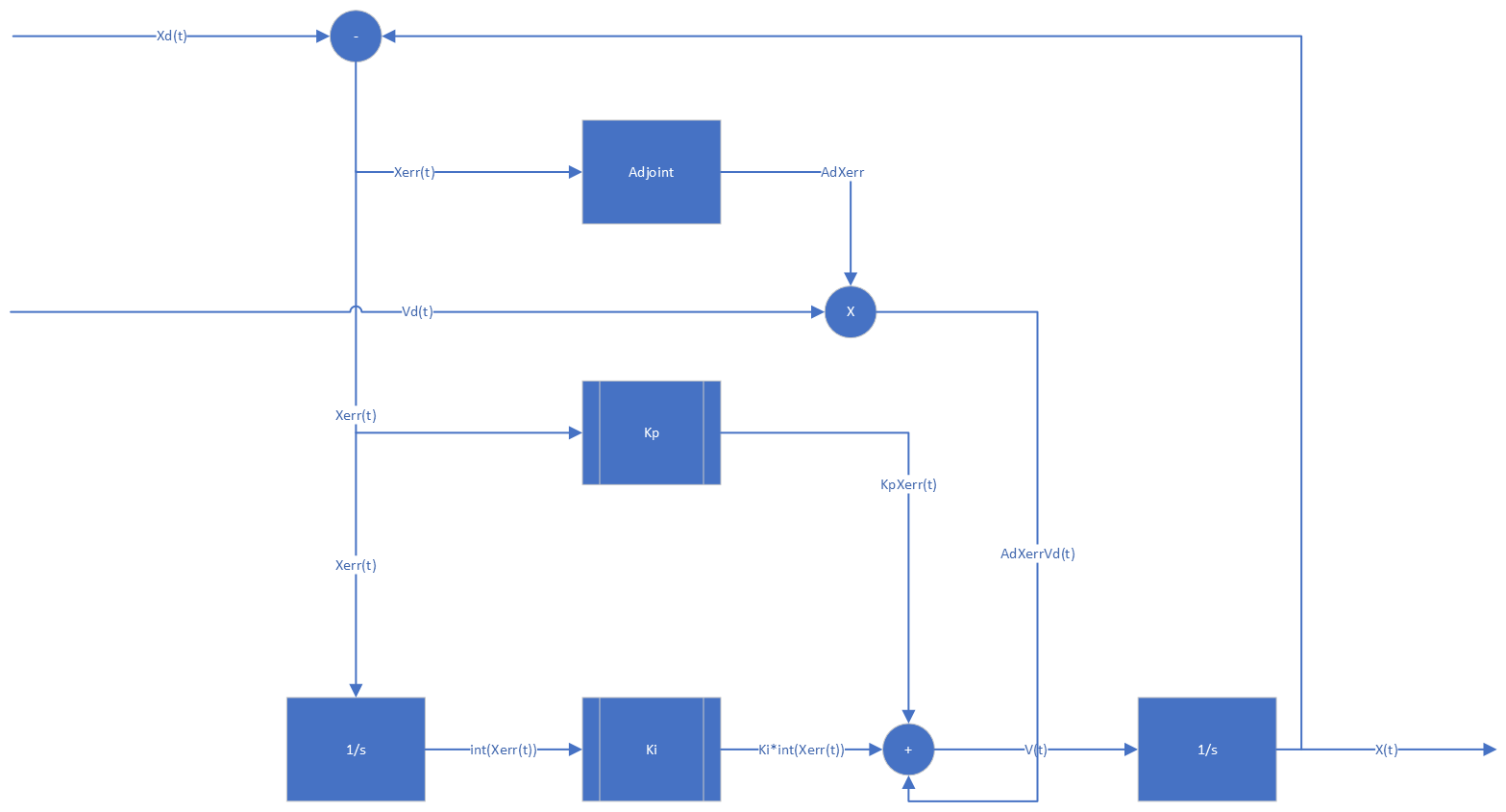
This is a Feedforward Controller with a PI Feedback Controller. The first term is a feedforward term where the commmand velocity is relative to the desired velocity. The second one is the proportional control, where the command velocity is proportional to the difference between the actual pose and desired pose. The last one is the integral term, that the command velocity is proportional to the sum of all errors.
Results
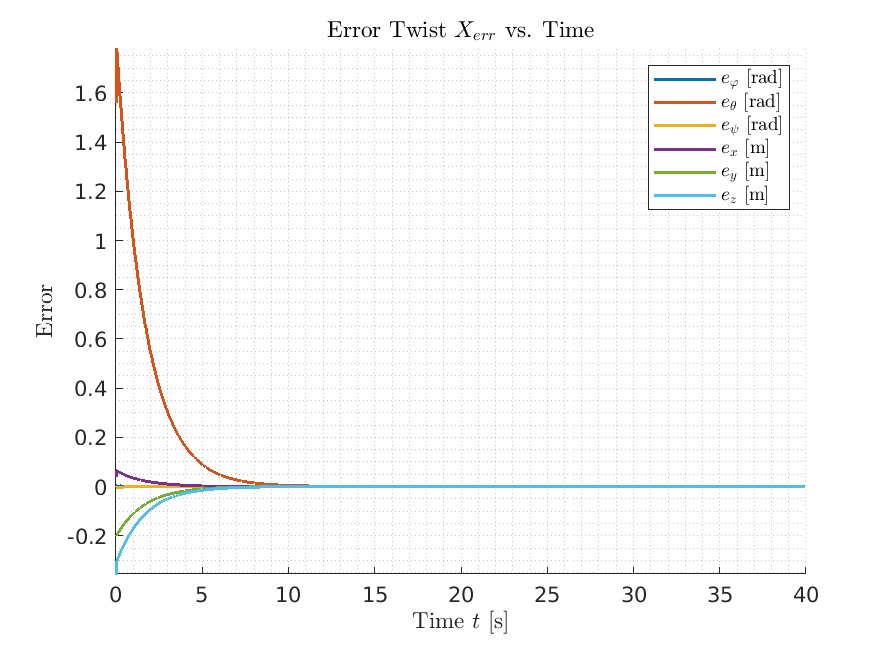
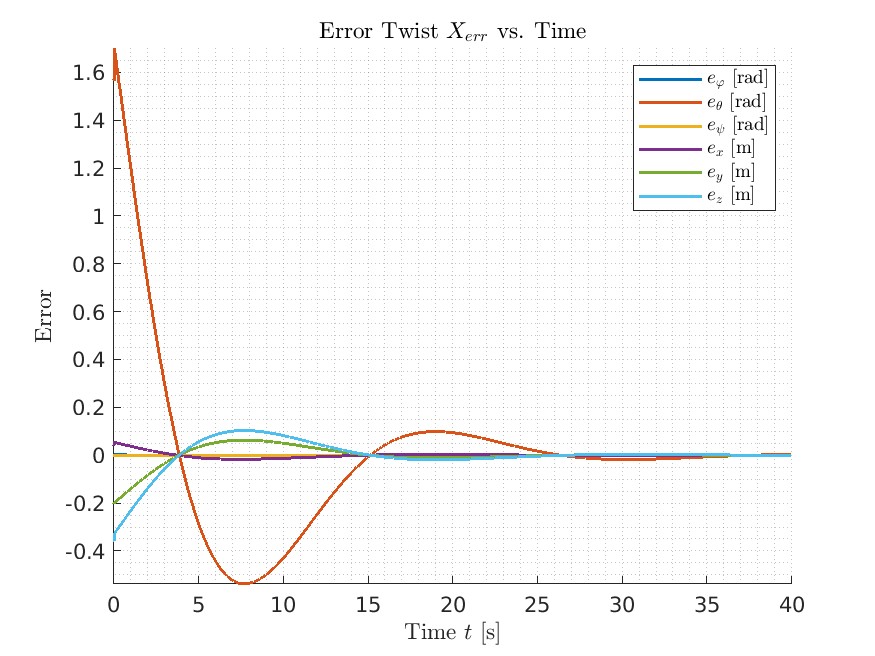
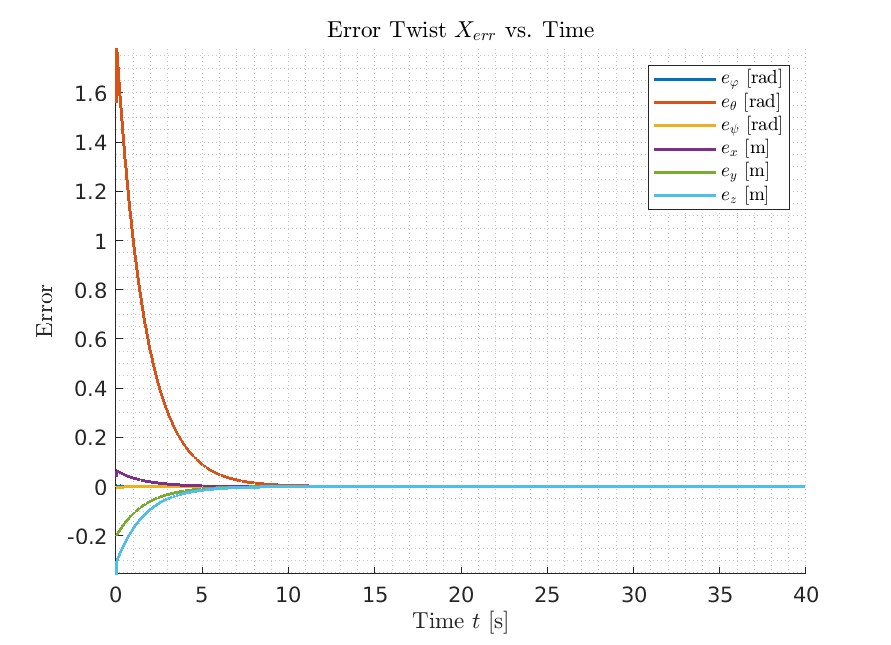
As shown in the error plot in the three senarios, on Best and New Task, after it converges, it stays on the planned path. And for the Overshot, it oscillates around the planned path and converges much slower than the other two scenarios.
Best
Overshoot
New Task
Challenges
- Finding Optimal
KpandKi: Discovering the ideal values forKiandKpposes a challenge in designing controllers that excel in various scenarios. Achieving optimal performance necessitates an iterative process for each parameter. Theoretical values alone often fall short of delivering the best results. To overcome this challenge, I invest a substantial amount of time in conducting extensive experiments. This approach allows me to identify and refine the most effective values for the controller, ensuring optimal performance across diverse situations.